BG SBLC Monetization

Understanding Liens: Types, Uses, and Key Insights to Protect Your Assets
December 9, 2024
What is Bank Payment Undertaking (BPU)? Benefits, Process, and Case Study
December 17, 2024BG SBLC Monetization
What is BG SBLC Monetization?
BG SBLC Monetization is a financial process where a Bank Guarantee (BG) or Standby Letter of Credit (SBLC) is used as collateral to obtain funding or a loan. This process is also known as BG/SBLC funding While the primary purpose of an SBLC is to serve as a security instrument, it can also be leveraged or “monetized” to access liquidity. The monetized funds can either be a recourse or nonrecourse loan.
Artley Finance (HK) Limited is the leading BG SBLC monetizer and has developed relationships with some of the top banks in the world to Monetize Standby Letters of Credit and Bank Guarantees for clients worldwide. We can arrange and assist clients in monetizing their financial instruments (Bank Guarantees and Standby Letters of Credit) from rated banks.
Our BG SBLC monetization rate is 80% LTV which is the best rate in the industry, and above all, all our bank instruments (Bank Guarantees and SBLCs) are issued by top AAA-rated banks such as HSBC Hong Kong, CitiBank New York, Barclays Bank London, Credit Suisse etc.

Step-by-Step Process for BG SBLC Monetization:
- Issuance of BG SBLC: A reputable bank issues the BG/SBLC on behalf of a client (the applicant) for a specific amount, guaranteeing that payment will be made to the beneficiary if the applicant defaults.
- Transfer of the BG/SBLC to a Monetizer: The holder of the BG/SBLC, often a business or individual, transfers or assigns the BG/SBLC to a monetizing entity (usually a financial institution like Artley Finance (HK) Limited, private lender, or investor) for a certain term or value.
- Monetizer’s Review: The monetizer reviews the BG/SBLC to confirm that it is valid, unconditional, and issued by a credible bank. The value and terms of the BG/SBLC are assessed, including the term of the BG/SBLC, bank rating, and other details.
- Funding Release: Once verified, the BG/SBLC monetizer provides a loan or cash advance to the BG/SBLC holder, typically at a percentage of the BG/SBLC’s face value (between 60% to 90%). The monetized funds can be used for business expansion, investments, or other financial purposes.
- Repayment: Depending on the agreement, the SBLC holder may repay the loan with interest, or the monetizer may draw upon the SBLC when it matures.
Top Benefits of BG SBLC Monetization
Access to Liquidity: SBLC holders can convert financial instruments into cash or credit for immediate use.
Flexible Financing Options: BG SBLC monetization offers an alternative to traditional bank loans, particularly for those with limited financing options.
Types of BG/SBLC Monetization:
- Recourse: The BG/SBLC holder is responsible for loan repayment.
- Non-Recourse: The holder is not required to repay the loan.
Why Monetize an Bank Instruments?
- Access to Liquidity: BGs and SBLCs holders can convert their instrument into cash or credit.
- Flexible Financing: BG SBLC monetization offers an alternative to traditional bank loans, particularly for those with limited financing options.
BG/SBLC Monetization Risk:
- BG SBLC Fraud: Fraudulent or non-genuine BG or SBLC can result in significant financial losses.
- Bank Reputation: If the issuing bank has a lower credit rating, the BG SBLC will not be monetized at favorable rates. BGs and SBLCs from low rated banks in Africa, Asia or South America cannot be monetized. This is why it is very important to work with genuine bank instrument providers like Artley Finance (HK) Limited with decades of experience and credibility.
SWIFT Network for BG/SBLC Funding:
Artley Finance (HK) Limited simplifies the monetization process using the SWIFT Network. The financial instrument (BG/SBLC) is delivered via SWIFT MT799, followed by SWIFT MT760, ensuring a secure and reliable bank-to-bank transaction.
Real-World Example of an SBLC in Action:
Scenario: A European importer (Company A) agrees to purchase $10 million worth of machinery from a Chinese exporter (Company B). This is their first transaction, introducing trust concerns.
Problem:
- Company B requires payment assurance to ship the goods.
- Company A wants to avoid upfront payment, fearing non-delivery.
Solution: Company A arranges for its bank to issue a $10 million SBLC in favor of Company B. The SBLC ensures payment to Company B if Company A defaults. This setup secures the transaction for both parties.
Understanding Standby Letters of Credit (SBLC)
A Standby Letter of Credit (SBLC), abbreviated as SBLC, is a financial instrument that guarantees payment from a bank to a seller if the buyer defaults on a contract. SBLCs are often used in international and domestic trade to build confidence between parties and to help businesses secure contracts.
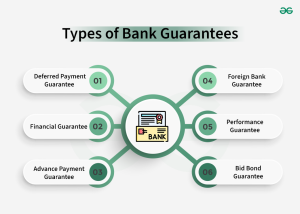
Types of SBLC:
1. Financial Standby Letter of Credit
- Purpose: Guarantees that the exporter (beneficiary) will receive payment for goods or services within the agreed-upon timeframe if the importer (applicant) fails to pay.
- Use Case: Often used in international trade to secure payments for goods or services.
2. Performance Standby Letter of Credit
- Purpose: Guarantees that the applicant will fulfill their obligations under a contract (usually related to project completion). If the applicant defaults, the bank compensates the beneficiary.
- Use Case: Common in construction or large infrastructure projects to ensure the completion of work within the specified time.
3. Advance Payment Standby Letter of Credit
- Purpose: Protects the beneficiary if the applicant fails to make an agreed-upon advance payment, ensuring that the beneficiary still receives the payment.
- Use Case: Frequently used when suppliers or service providers require advance payments before starting a project or delivering goods.
4. Insurance Standby Letter of Credit
- Purpose: Guarantees payment if the applicant fails to pay for insurance obligations or commitments made under an insurance contract.
- Use Case: Provides security for insurance companies in case of non-payment by their clients.
5. Counter Standby Letter of Credit
- Purpose: Issued by one bank to another bank in a different country, requesting that the second bank issue a local SBLC for the bank’s client.
- Use Case: Common in cross-border transactions where the issuing bank does not have a local presence, so it instructs a foreign bank to issue the SBLC on its behalf.
6. Tender Standby Letter of Credit (Bid Bond SBLC)
- Purpose: Protects the beneficiary (usually a project owner) from non-performance or failure of the applicant (usually a contractor) to complete the project after being awarded a tender.
- Use Case: Often required in government or public-sector projects to ensure that contractors awarded bids perform their obligations.
7. Direct Pay Standby Letter of Credit
- Purpose: Ensures direct payment to the beneficiary if the applicant fails to make timely payments due to financial instability.
- Use Case: Used in cases where the applicant may be at risk of default, such as in large-scale capital-intensive projects or public infrastructure.
As you can see from the above, SBLCs are bank guarantees issued by financial institutions that promise to pay the beneficiary in case the applicant (the party requesting the SBLC) defaults on their obligations. And Each type of SBLC is tailored to mitigate different risks, making them versatile instruments in both financial and contractual obligations.
Understanding Bank Guarantees (BG)
A Bank Guarantee (BG) is a financial instrument issued by a bank on behalf of a client, ensuring the client’s financial obligations to a third party will be met. If the client defaults or fails to fulfill the agreed-upon terms, the bank promises to compensate the beneficiary up to the specified amount.
Bank Guarantee (BG) Types:
1. Financial Guarantee:
Ensures payment obligations are met.
2. Performance Guarantee:
Ensures performance obligations (e.g., completing a project) are fulfilled.
- Use Cases: Common in international trade, construction contracts, large-scale procurement and BG monetization.
Parties Involved in a bank guarantee transaction:
-
- Applicant: The party requesting the guarantee (typically the buyer or contractor).
- Beneficiary: The party receiving the guarantee (typically the seller or project owner).
- Bank: The institution providing the guarantee.
Bank Guarantees provide financial security and foster smoother business transactions by reducing counterparty risk.
BG SBLC COSTS:
The costs associated with obtaining and monetizing a Bank Guarantee (BG) / Standby Letter of Credit (SBLC) can vary depending on several factors, including the issuing bank, the intermediaries involved, and the terms of the monetization process. Below are the typical costs involved:
1. Issuance Fees
- Issuing Bank Fees: Financial institutions typically charge a fee to issue the BG/SBLC. This fee is usually a percentage of the total value of the BG/SBLC and can range between 1% to 10% of the face value, depending on the institution, the size of the SBLC, and the applicant’s creditworthiness. Fees may also depend on whether the SBLC is issued for a short or long term. However, Artley Finance (HK) Limited, our BG/SBLCissuing fee is 4% of the BG/SBLC face value per year.
- Annual Fees: If the SBLC is issued for more than a year, the institution may charge annual renewal fees, usually similar to the initial issuance cost.
2. Intermediary Fees
- Broker or Facilitator Fees: In many cases, an SBLC is obtained or monetized through intermediaries such as brokers or facilitators. These charge commissions for arranging the SBLC issuance or monetization, typically 2% of the BGs SBLC’s value. Artley Finance (HK) Limited brokers are paid 2% for each deal they bring to us, and our brokers are protected against circumvention.
3. Monetization Costs
- Discount Rate: When monetizing an SBLC or bank guarantee, the monetizer typically offers less than the full face value of the instrument. This “discount” can range from 10% to 40%, meaning you may receive 60% to 90% of the SBLC’s face value, depending on the terms of the monetization, the issuing bank’s reputation, and the risk involved.
- Processing Fees: The monetizing entity might charge a processing or transaction fee, usually a small percentage of the funds being provided.
4. Legal and Administrative Costs
Legal advice may be needed for drafting or reviewing the financial instrument contract and agreements related to its monetization. Some administrative costs may be incurred to cover notarization and other documentation requirements, particularly if international parties are involved. These fees vary depending on the jurisdiction but can be in the region of a few thousand dollars.
Interest and Repayment Costs (for Recourse Monetization)
Interest Rates: If the SBLC monetization is structured as a loan (recourse), the holder may need to repay the loan with interest. Interest rates depend on market conditions, the financial institution, and the creditworthiness of the applicant.
Chart of Typical SBLC Costs:
DESCRIPTION OF BANK INSTRUMENT and NON-RECOURSE PROJECT FUNDING
| Instrument Type: | Standby Letter of Credit (SBLC), Cash Backed |
| Total Face Value: | $10,000,000.00USD (Ten Million USD) |
| Currency: | $USD |
| Issuing Bank: | HSBC Hong Kong or Barclays Bank London |
| Age/Validity: | One (1) Year and One (1) Day |
| Leasing Price: | 4% (to be deducted from approved funds) |
| Bank Transmission fee: | $80,000 (Sixty Thousand US Dollars) To be paid upfront |
| Arrangement Fee: | $10,000 (Ten Thousand US Dollars) To be paid upfront |
| Monetization fee: | $250,000 (Two Hundred & Fifty Thousand Dollars) To Be Taken from the Monetized Funds |
| Project Fund To Value: | $8,000,000.00 (Eight Million USD) Non-Recourse Project Funding to be paid out. |
| Payment Schedule: | Within five (5) banking days after confirmation, verification and authentication of the Swift MT760, the Project Owner will receive 80% net of the Face Value via direct cash wire transfer (MT103) |
| Funding Repayment: | Approved Project Funds are Non-Recourse. |
| Intermediary Fee: | 2% Commission paid to brokers at closing: (This applies only when deal was introduced by a broker or intermediary) |
| Delivery: | By Swift MT760 to Project Funder‘s Bank account |
| Hard Copy: | Bank Bonded Courier within Seven Banking Days |
FAQs About BG SBLC Monetization
What is BG SBLC Monetization?
BG SBLC Monetization, also known as bank guarantee funding, involves converting a Bank Guarantee (BG) or Standby Letter of Credit (SBLC) into cash or credit by using it as collateral.
How Does BG SBLC Monetization Work?
The process includes a bank or financial institution like Artley Finance (HK) Limited issuing the instrument, transferring it to a monetizer, evaluating the instrument, funding release, and eventual repayment or settlement.
What Are the Risks Involved?
Fraudulent instruments and low-rated issuing banks can lead to significant financial risks. Partnering with reputable companies like Artley Finance (HK) Limited mitigates such risks.
While Artley Finance (HK) Limited has over five decades of experience and unparalleled expertise across the entire range of trade finance and project financing, nowhere are our experience and innovation more evident than in the monetization of bank financial instruments, especially Standby Letters of Credit (SBLC) and bank guarantees (BG). Therefore, there is no better partner for monetizing Standby Letter of Credit (SBLC) in the world than Artley Finance (HK) Limited.
If you’re ready to monetize your BG or Standby Letter of Credit, click here to submit a Standby Letter of Credit (SBLC) Monetization request and we will revert back to you with our complete monetization package within 24 hours. Alternatively, you can send an email to our trade finance specialists finance@artleyfinance.com


